
However, the second one is simpler compared to the first. Adding to this, there is less power dissipation in this 2 transistor schematic and it is more reliable compared to the other. The first schematic shows a circuit which switches states faster than the second. You can connect the leftmost transistor as shown, but be aware that it must be a special type of NPN. The collector-emitter junction acts as a short circuit, so there is little current left for the output when the input is high. 1 Overview edit Most logic optimization result in a sum-of-products or product-of-sums logic expression.
Inverter transistor diagram software#
It is fully turned on, the maximum amount of current passes through the collector with respect to the base current. Want to Make an Inverter Circuit Diagram EdrawMax is able to create free asset mapping and models for software development teams with ease.
The transistors work biased in reverse active mode and in saturation respectively. When the input A is low, no current passes through to the rightmost transistor. The described operation takes place when the input A is high. This current activates the transistor on the right side, pulling low the inverted output. The emitter is used as an input and as long as it is high, current will flow through its collector. It is a specialised type of a BJT which is commonly used in TTL logic design. To analyze the circuit in more detail, I connected the gates of the MOSFETs to an oscilloscope to compare the waveforms at the output and input of the MOSFET circuit.The transistor on the left is not a usual bipolar transistor. The power inverter produced about 190V AC, which was enough to power a 60W incandescent lightbulb fairly brightly. When I built this circuit, I used a 12V battery providing 4.5A of current. It’s only close because the transformer’s efficiency will probably be around 70%, so in reality the output current will be closer to about 0.63A. But in general, if you have a 100VA, 110V transformer, then you should be able to get close to 100VA / 110V = 0.9A. The size of the mains transformer and the amount of current that can be drawn from the battery will govern how much AC power is available.

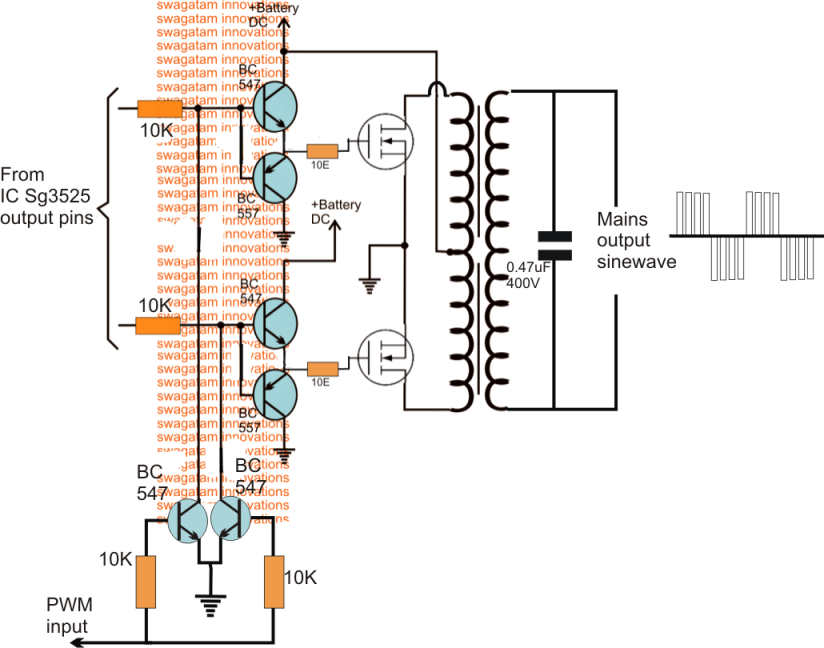
Since T1 is an inductive load, we need to have two flyback diodes (D1 and D2) to prevent a back EMF spikes from killing the MOSFET transistors. The drains of the MOSFET transistors are connected to the +12V and -12V sides of mains transformer T1. I found that the MOSFETs need to be low Rds types such as the IRF540 MOSFET transistor or IRLZ44 MOSFET transistor. The MOSFET transistors are switched on and off by the square wave generated by the 555 timer. It can be set to 50Hz or 60Hz.Ī half-bridge MOSFET circuit is connected to the output of the 555 timer. The frequency is controlled by potentiometer R5. Transistor Q1 is an inverting transistor to give a 180º phase shift. The 50Hz oscillator is provided by the 555 timer. The circuit is outlined in the block diagram below. Here is a 100 watt power inverter circuit with diagram and schematic using CD 4047 IC that generates 100 Hertz pulses and four transistors. We are going to build a power inverter that takes its input power from a 12V battery, and outputs a 110V/230V AC current. Failure to do so could result in fire, injury, or even death. This project should only be built if you are trained to work with high voltage electronics. As an example, if the power inverter’s output were rated at 100VA and 110V, the output current would be 100VA / 110V = 0.9A.Ī WORD OF CAUTION: This project will involve working with high voltages. To do this, find the power inverter’s VA rating and voltage rating. Otherwise the power inverter might not be able to supply enough current to power your devices. It’s important to calculate the current that can be supplied by a power inverter. Power inverters range from simple DIY circuits using a few transistors and a transformer, to expensive commercial units using microcontrollers to generate PWM sine waves. Power inverters are also an important part of un-interrupted power supplies. They are also used in systems where the mains power is supplied by solar panels or wind generators. Power inverters are typically used to create a mains power backup from a set of 12V batteries in the event of a power outage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
